|
|
|
|
|
|
Array index The number that identifies a particular element in an array is called the index. If the number is actually a variable, then this is called an index variable. An index must be an integer (i.e. of type int), because it refers to a particular element in an array ?i.e. element 3 or element 0 or element 2000, never anything like element 2.5! This Java applet will generate an error message: The error produced is:import java.applet.Applet; 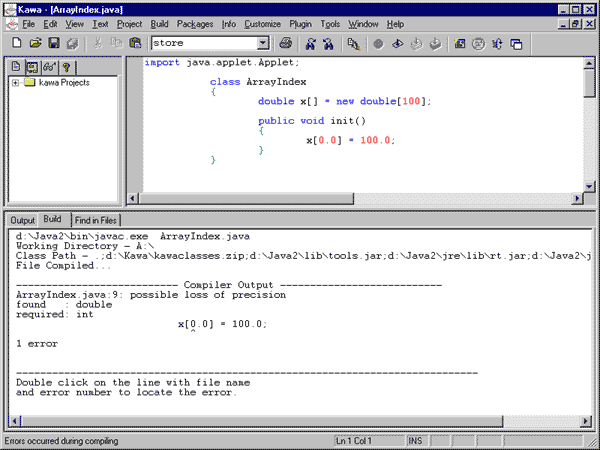 This
is because "0.0" (zero point zero) is not the same to the compiler as "0"
(zero). "0.0" is a floating point number, while "0" is an integer.
The following six sets of Java statements all have the same effect: they set the variable x equal to the 3rd element of the array array1 (don't forget: the third element has index 2, not 3): int x = array1[5-3]; int index =
2;
int index =
5;
int index =
5 - 3;
int x = array1 [(int)2.0]; You
should look at each of these lines and ensure that you understand why it
produces the result that it does. The last line introduces something you
may not have used before: the use of a data type (in this case int)
before an item of a different type (in this case the number 2.0,
which is a double).
As you may recall from a previous unitt, this form of expression is called a cast. It is an instruction to the compiler to treat evaluate an expression to a value of the stated type ?converting from some other type. In this case, an array index has to be an integer, so we tell the compiler to treat 2.0 as an integer. What do you think would happen if we said: Of
course, 2.5
can't be an integer. In fact what happens in this
case is that the compiler chops off the decimal part of the number, and
makes it 2.
You
can't use the cast to convert anything to anything else. For example, the
compiler will produce an error message if you try to compile
int x = (int)"hello"; because "hello" simply cannot be converted to an integer.
RITSEC - Global Campus
|