|
|
|
|
|
|
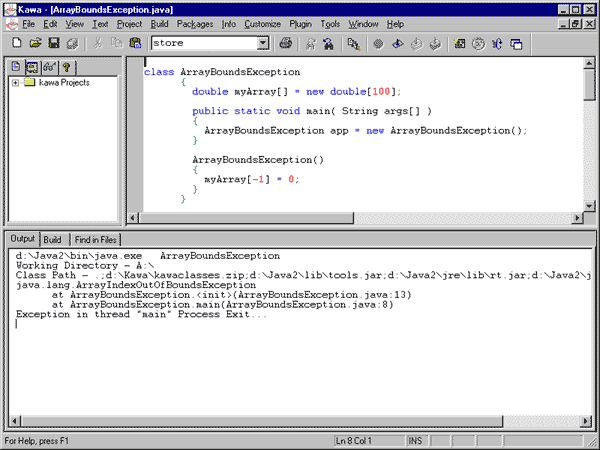
Array bounds exceptions An error will occur if an index is given for an array, which is either negative, or greater than the index of the last element of the array (i.e. a value of <array>.lengthor greater). Such an error is called an array bounds exception. The program must not attempt to read or change the value of an array element that does not exist. For example, no array can have an element whose index is less than zero Suppose we define an array of doubles like this: double myArray[] = new double[100]; Then
all the following lines will cause a run time error (that is, the program
will compile correctly, but when executed will stop with an error message):
myArray[] = 0; Note
that the compiler does not detect these errors; the error is not
noted until the program is executed. This is true even of the first line,
which is manifestly incorrect.
Consider the following
application:
class ArrayBoundsExceptionThe error displayed when this application is run as follows:
RITSEC - Global Campus
|